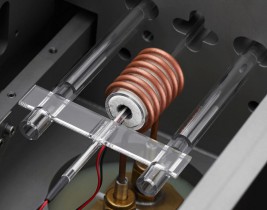
Quenching Dilatometers
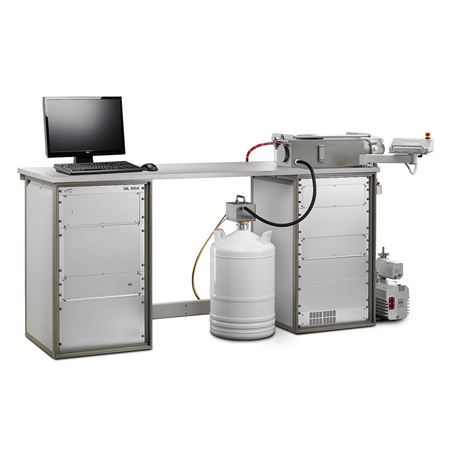
A family of quenching dilatometers used to study the heat treatment of steel and metal alloys to identify the heating rate, the quenching rate and the isothermal dwell times necessary to yield the crystalline structure to meet the required physical properties.
The QHM-DT805 Series comprises of four models: QHM-DT805L, QHM-DT805A are quenching dilatometers, QHM-DT805A/D is a quenching with the capability to deform the specimen by compression, and QHM-DT805A/D/T that can also stretch it in tension mode.
All four instruments are fully automated, self-contained units used to measure dimensional changes under extreme conditions of controlled heating and cooling.
In the quenching mode the sample, solid or hollow, is inductively heated to a temperature plateau and is then cooled at an user-defined (linear or exponential) cooling rate. The inductive heating with constant sinus frequency is power controlled by amplitude adjustment for superior temperature homogeneity in the sample. The phase transformation occurring in the continous cooling process or in the isothermal dwell, with or without compression/tensile stress, is indicated by the measured change in length. An array of cooling or isothermal curves represents a continous-cooling-transformation (CCT) diagram or an isothermal time-temperature-transformation (TTT) diagram, respectively. DIL 805A represents today the benchmark for determining these dimensional changes and phase transitions. Operating from -160°C up to 1700°C (in two different furnace configurations) with peak heating rates of up to 4000°C/s and peak cooling rates of 4000°C/s, can closely simulate the material response for any production or heat treatment process. QHM-DT805A allow using a choice of inert and reducing gases as cooling gas. Particularly helium is an effective cooling gas that provides a homogeneous temperature distribution in the metallic sample.
The DIL 805A/D, on top of the quenching mode, is distinguished by its capability to deform the specimen with controlled deformation rates of of 0.01 to 200 mm/s. Used to optimize steel processes like hot or cold rolling, QHM-DT805A/D allows to develop time-temperature-transformation diagrams after deformation (DTTT) and is also used to examine creep and relaxation processes.
DIL 805A/D/T further extends the capabilities to alternate tensile and compressive loading to emulate mill processing. Moreover, tensile loading to fracture lends additional information about material’s final performance and allows to generate true-stress vs true-strain or stress/strain cycling plots.
|
QHM-DT 805L |
QHM-DT 805A |
QHM-DT 805A/D |
QHM-DT 805A/D/T |
|
| Temperature
Range: (sample dependent) |
-150°C
to 1300°C |
-150°C
to 1300°C |
-150°C to 1300°C 50°C to 1700°C |
-150°C to 1300°C 50°C to 1700°C |
| Heating principle: | inductive, power controlled by amplitude adjustment with constant sinus frequency | inductive, power controlled by amplitude adjustment with constant sinus frequency | inductive, power controlled by amplitude adjustment with constant sinus frequency | inductive, power controlled by amplitude adjustment with constant sinus frequency |
| Sample material: | Electrically conductive hollow or solid body | Electrically conductive hollow or solid body | Electrically conductive hollow or solid body | Electrically conductive hollow or solid body |
| Sample Geometry: | OD 4mm Length 10mm |
OD 4mm
optional: OD 1mm to
22mm |
OD 5mm Length 10mm optional: OD 1mm to 22mm |
OD 5mm Length 10mm optional: OD 1mm to 22mm |
| Length Resolution: | 50 nm | 50 nm | 50 nm | 50 nm |
| Temperature Resolution: | 0.05°C | 0.05°C | 0.05°C | 0.05°C |
| Atmosphere: | inert gas, vacuum, air | inert gas, vacuum, air | inert gas, vacuum, air | inert gas, vacuum, air |
| Max. Heating
rate Max. Cooling rate: |
4000°C/sec 4000°C/sec |
4000°C/sec 4000°C/sec |
100
°C/sec 100°C/sec |
100
°C/sec 100°C/sec |
| Deformation force: | up to 20.0 kN | up to 8.0 kN | ||
| Deformation rate: | 0.01 – 200 mm/sec | 0.01 – 20 mm/sec | ||
| Strain rate φ: | 0.001 – 20.0 s-1 | 0.001 – 20.0 s-1 | ||
| True strain φ: | 0.05 – 1.2 | 0.05 – 1.2 | ||
| Minimum Gauge Length: | 3 mm | 3 mm | ||
| Number of deformation steps: | any number | any number | ||
| Pause between deformation steps: | 40 msec | 40 msec | ||
| Data recording rate: | 1000 redcordings/s for each parameter | 1000 redcordings/s for each parameter | 30000 redcordings/s for each parameter | 30000 redcordings/s for each parameter |
QHM-DT 805A Quenching Dilatometer – Measurement Principle
QHM-DT805A Quenching Dilatometer – Measurement Principle
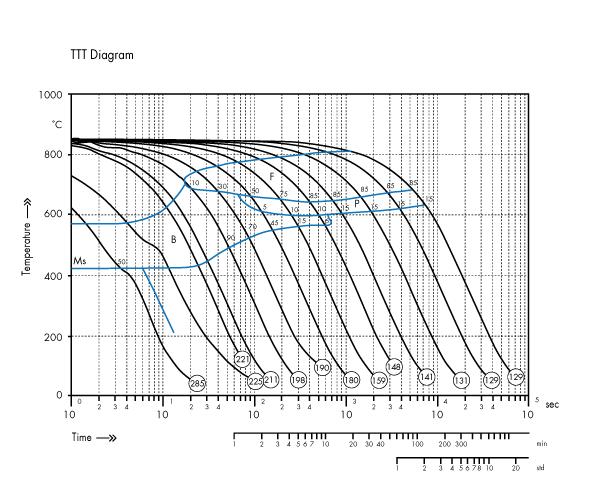
The QHM-DT805A(*) is used to observed dimensional changes under extreme conditions of controlled heating and cooling. A solid or a hollow sample is inductively heated to a temperature plateau and is then continuously cooled with different (linear or exponential) rates. The phase transformation occurring in the continuous cooling process or in the isothermal plateau (which may also be a multi-step transition) is indicated by the measured change of length. An array of cooling curves represent a continuous or an isothermal TTT diagram (Time-Temperature- Transformation diagram). The beginning and end of the transformation indicate the alloy phase boundaries, e.g. ferrite, carbide, graphite, pearlite, bainite, martensite or other eutectoid phase batches.
(*): The “A” designation is from the German “Abschreck” for quenching
QHM-DT 805A/D, Quenching and Deformation Dilatometer– Measurement Principle
QHM-DT805A/D, Quenching and Deformation Dilatometer– Measurement Principle
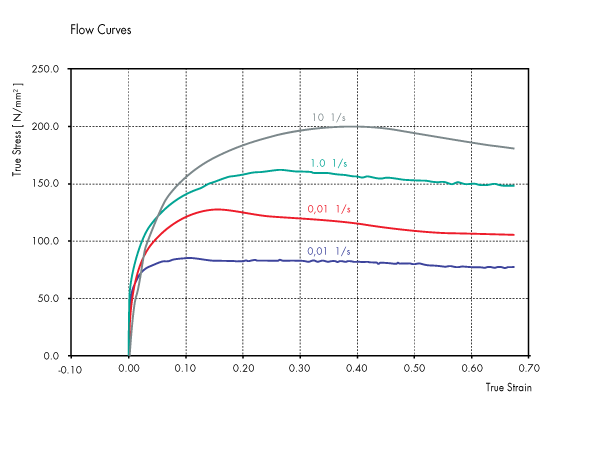
The QHM-DT 805A/D extends the principle of the QHM-DT 805A to also include controlled deformation. At a user-defined temperature a solid sample is compressed with various deformation programs (e.g. linear, multi-level stage, with constant deformation rate, with constant force). As with the quenching dilatometer it is now possible to carry out a cooling process in order to create a DTTT diagram (Time-Temperature-Transformation diagram after Deformation). The QHM-DT 805A/D is also used to examine creep and relaxation processes.
- Overview
-
The QHM-DT805 Series comprises of four models: QHM-DT805L, QHM-DT805A are quenching dilatometers, QHM-DT 805A/D is a quenching with the capability to deform the specimen by compression, and QHM-DT 805A/D/T that can also stretch it in tension mode.
All four instruments are fully automated, self-contained units used to measure dimensional changes under extreme conditions of controlled heating and cooling.
In the quenching mode the sample, solid or hollow, is inductively heated to a temperature plateau and is then cooled at an user-defined (linear or exponential) cooling rate. The inductive heating with constant sinus frequency is power controlled by amplitude adjustment for superior temperature homogeneity in the sample. The phase transformation occurring in the continous cooling process or in the isothermal dwell, with or without compression/tensile stress, is indicated by the measured change in length. An array of cooling or isothermal curves represents a continous-cooling-transformation (CCT) diagram or an isothermal time-temperature-transformation (TTT) diagram, respectively. QHM-DT 805A represents today the benchmark for determining these dimensional changes and phase transitions. Operating from -160°C up to 1700°C (in two different furnace configurations) with peak heating rates of up to 4000°C/s and peak cooling rates of 4000°C/s, can closely simulate the material response for any production or heat treatment process. QHM-DT805A allow using a choice of inert and reducing gases as cooling gas. Particularly helium is an effective cooling gas that provides a homogeneous temperature distribution in the metallic sample.
The QHM-DT805A/D, on top of the quenching mode, is distinguished by its capability to deform the specimen with controlled deformation rates of of 0.01 to 200 mm/s. Used to optimize steel processes like hot or cold rolling, QHM-DT805A/D allows to develop time-temperature-transformation diagrams after deformation (DTTT) and is also used to examine creep and relaxation processes.
QHM-DT 805A/D/T further extends the capabilities to alternate tensile and compressive loading to emulate mill processing. Moreover, tensile loading to fracture lends additional information about material’s final performance and allows to generate true-stress vs true-strain or stress/strain cycling plots.
- Specifications
-
QHM-DT 805L
QHM-DT 805A
QHM-DT 805A/D
QHM-DT 805A/D/T
Temperature Range:
(sample dependent)-150°C to 1300°C
50°C to 1500°C-150°C to 1300°C
50°C to 1700°C-150°C to 1300°C
50°C to 1700°C
-150°C to 1300°C
50°C to 1700°C
Heating principle: inductive, power controlled by amplitude adjustment with constant sinus frequency inductive, power controlled by amplitude adjustment with constant sinus frequency inductive, power controlled by amplitude adjustment with constant sinus frequency inductive, power controlled by amplitude adjustment with constant sinus frequency Sample material: Electrically conductive hollow or solid body Electrically conductive hollow or solid body Electrically conductive hollow or solid body Electrically conductive hollow or solid body Sample Geometry: OD 4mm
Length 10mmOD 4mm optional: OD 1mm to 22mm
Length 10mmOD 5mm
Length 10mm optional: OD 1mm to 22mmOD 5mm
Length 10mm optional: OD 1mm to 22mmLength Resolution: 50 nm 50 nm 50 nm 50 nm Temperature Resolution: 0.05°C 0.05°C 0.05°C 0.05°C Atmosphere: inert gas, vacuum, air inert gas, vacuum, air inert gas, vacuum, air inert gas, vacuum, air Max. Heating rate
Max. Cooling rate:4000°C/sec 4000°C/sec 4000°C/sec
4000°C/sec100 °C/sec
100°C/sec100 °C/sec
100°C/secDeformation force: up to 20.0 kN up to 8.0 kN Deformation rate: 0.01 – 200 mm/sec 0.01 – 20 mm/sec Strain rate φ: 0.001 – 20.0 s-1 0.001 – 20.0 s-1 True strain φ: 0.05 – 1.2 0.05 – 1.2 Minimum Gauge Length: 3 mm 3 mm Number of deformation steps: any number any number Pause between deformation steps: 40 msec 40 msec Data recording rate: 1000 redcordings/s for each parameter 1000 redcordings/s for each parameter 30000 redcordings/s for each parameter 30000 redcordings/s for each parameter - Measurement Principle
-
QHM-DT 805A Quenching Dilatometer – Measurement Principle
QHM-DT805A Quenching Dilatometer – Measurement Principle

The QHM-DT805A(*) is used to observed dimensional changes under extreme conditions of controlled heating and cooling. A solid or a hollow sample is inductively heated to a temperature plateau and is then continuously cooled with different (linear or exponential) rates. The phase transformation occurring in the continuous cooling process or in the isothermal plateau (which may also be a multi-step transition) is indicated by the measured change of length. An array of cooling curves represent a continuous or an isothermal TTT diagram (Time-Temperature- Transformation diagram). The beginning and end of the transformation indicate the alloy phase boundaries, e.g. ferrite, carbide, graphite, pearlite, bainite, martensite or other eutectoid phase batches.
(*): The “A” designation is from the German “Abschreck” for quenching
QHM-DT 805A/D, Quenching and Deformation Dilatometer– Measurement Principle
QHM-DT 805A/D, Quenching and Deformation Dilatometer– Measurement Principle

The QHM-DT 805A/D extends the principle of the QHM-DT805A to also include controlled deformation. At a user-defined temperature a solid sample is compressed with various deformation programs (e.g. linear, multi-level stage, with constant deformation rate, with constant force). As with the quenching dilatometer it is now possible to carry out a cooling process in order to create a DTTT diagram (Time-Temperature-Transformation diagram after Deformation). The QHM-DT 805A/D is also used to examine creep and relaxation processes.